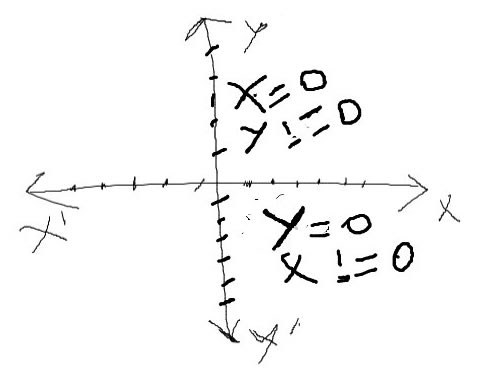
If x!=0 and y==0 then it will be in the y asix and
If y!=0 and x==0 then it will be in the x axis
that means you have to understand if what the value is equivalent to 0 then it will be in that axis
And one thing = means assignment operator if x=y then if x=5 then y=5
and == means comparison operator if x==y then if x==4 and y==5 then x!=y so it will be false
and if x=5 and y=5 then x==y and it is true
Reference:
http://www.allinterview.com/showanswers/17960/what-is-the-difference-between-and-in-c.html
http://www.mathsisfun.com/data/cartesian-coordinates.html
code:
#include<cstdio>
int main()
{
float x,y;
while(scanf("%f %f",&x,&y)==2)
{
if(x==0 && y==0)
printf("Origem\n");
else if(y==0 && x!=0)
printf("Eixo X\n");
else if(x==0 && y!=0)
printf("Eixo Y\n");
else if(x>0 && y>0)
printf("Q1\n");
else if(x<0 && y>0)
printf("Q2\n");
else if(x<0 && y<0)
printf("Q3\n");
else
printf("Q4\n");
}
return 0;
}
and like this can do
#include<cstdio>
int main()
{
float x,y;
while(scanf("%f %f",&x,&y)==2)
{
if(x==0 && y==0)
printf("Origem\n");
else if(y==0)
printf("Eixo X\n");
else if(x==0)
printf("Eixo Y\n");
else if(x>0 && y>0)
printf("Q1\n");
else if(x<0 && y>0)
printf("Q2\n");
else if(x<0 && y<0)
printf("Q3\n");
else
printf("Q4\n");
}
return 0;
}
Here in this code you have to think about the flow which normally starts from the 0 and the compiler starts punctuating the code from Zero 0.
logic flow can be start from 0 then can be happen through greater than or equal
It’s better to do in C/C++ main format