If subclass has the same method s declared in the parent class, it is known as method overriding in java.
– Method override is used for runtime polymorphism
– Method overriding is used to provide specific implementation of a method that is already provided by its super class.
Rules –
1.Method must have same name is in the parent class
2. method must have separator as in the parent class
3. Must be IS-A relationshp
understanding the problem without method overriding:
public class Vehicles {
void run()
{
System.out.println("Vehicle is running");
}
static class Bike extends Vehicles{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Bike objectu=new Bike();
objectu.run();
}
}
}
Output:
Vehicle is running
Problem is that I have to provide a specific implementation of run() method in subclass that is why we use method overriding.
Example of method overriding:
public class Vehicles {
void run()
{
System.out.println("Vehicle is running");
}
class Bike2 extends Vehicles{
void run()
{
System.out.println("Bike is running safely");
}
}
//static class Bike extends Vehicles{
public void main(String[] args)
{
Bike2 objectus=new Bike2();
objectus.run();
}
//}
}
Output:
May be I did some wrong so output is not coming
Another example :
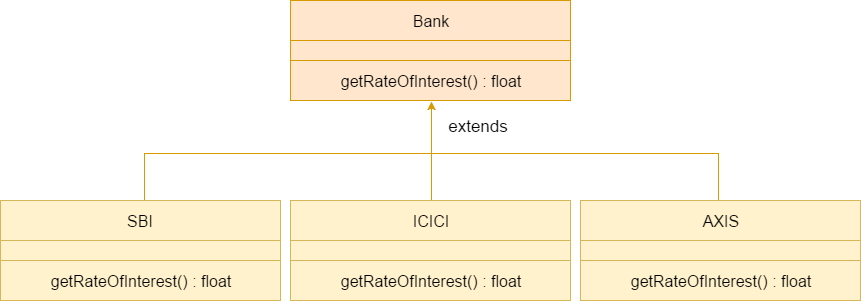
Bank.java
class Bank{
int getRateOfInterest(){return 0;}
}
class SBI extends Bank{
int getRateOfInterest(){return 8;}
}
class ICICI extends Bank{
int getRateOfInterest(){return 7;}
}
class AXIS extends Bank{
int getRateOfInterest(){return 9;}
}
Test2.java
class Test2{
public static void main(String args[]){
SBI s=new SBI();
ICICI i=new ICICI();
AXIS a=new AXIS();
System.out.println("SBI Rate of Interest: "+s.getRateOfInterest());
System.out.println("ICICI Rate of Interest: "+i.getRateOfInterest());
System.out.println("AXIS Rate of Interest: "+a.getRateOfInterest());
}
}
Output:
SBI Rate of Interest: 8 ICICI Rate of Interest: 7 AXIS Rate of Interest: 9
Reference:
http://www.javatpoint.com/method-overriding-in-java