Course link: https://www.linkedin.com/learning/git-branches-merges-and-remotes/format-the-commit-log?u=103775466
#Navigate the commit tree
Tree-ish architecture
SHA-1 hash
HEAD pointer reference
.git/HEAD
.git/refs/heads/master
Branch reference
Tag reference
Ancestry
Some common commands:
git log
git show commit_hash
Reference to a commit
Ancestry(parents):
commit_hash^
HEAD^
master^
HEAD~ or HEAD~1
git show HEAD^
Ancestry(Grandparents):
commit_hash^^
HEAD^^
master^^
HEAD~2
git show HEAD^^
Ancestry(Great grandparents):
commit_hash^^^
HEAD^^^
master^^^
HEAD~2
git show HEAD^^^
Tree
git ls-tree HEAD
git ls-tree HEAD^
git ls-tree HEAD assets
git ls-tree HEAD assets/
git log -3
git log –since=2019-01-01
git log –until=2019-01-01
git log –after=2.weeks –before =3.days
git log –author=”Zaki”
git log –grep=”Initial”
git log –grep=”bug”
git log commit_hash…HEAD
git log SHA..SHA
git log explorers.html
Format the commit log:
git log -p
git log –stat
git log –format=medium
git log –format=short
git log –format=oneline
–format=(can many things)
short
medium
full
fuller
email
raw etc.
git log –oneline
git log –graph
git log –graph –all –oneline –decorate
Create branch:
git branch new_feature
git branch
cat .git/HEAD
output: ref:refs/heads/master
ls -la .git/refs/heads
cat .git/refs/heads/master
cat .git/refs/heads/new_feature
Switch branches:
pwd
git branch
git checkout new_feature
git branch
cat .git/HEAD
output: ref: refs/heads/new_feature
git status
git commit -am “Modifies title of index.html”
-a for all changes in directory, m for messages
git log –oneline
git help log
git checkout master
git branch shorten_title
git checkout -b shorten_title
Without commiting you can not switch to another branch. There will be conflict.
Then thre options:
- Commit the changes to the current branch
- Remove the changes checkout the file again
- Stash the changes
Compare branches:
git diff master..new_feature
git diff new_feature..shorten_title
git diff shorten_title..new_feature
git branch
git checkout new_feature
git branch – -merged master lists branches merged into master
git branch – -merged = lists branches merged into HEAD
git branch – -no-merged = lists branches that have not been merged
Change branch name:
git help branch
git branch -m seo_title
Delete branches
git branch -d branch_to_delete (From other branch)
git branch -D delete_hobe
Reset Types
To move HEAD to a specific commit
Make the project look like it did back then
Types: Soft, Mixed, Hard
Soft: git reset –soft <tree-ish>
Mixed: git reset –mixed <tree-ish>
Hard: git reset –hard <tree-ish>
tree-ish= SHA/branch name
Rollback.
If we do that previous commit will be discarded
git checkout -b reset_branch shorten_title
git reset –soft HEAD^
git log –oneline -3
git status
git commit -m “Edit again”
git log –oneline -3
git show HASH
git reset –mixed HEAD^
git status
Git Merge
One branch to another
git branch
git checkout main
git diff main..seo_title
git branch –merged
git merge seo_title
always run merge with clean working directory
git log –graph –all –oneline –decorate
Strategies to reduce conflicts:
Keep lines short
Keep commits small and focused
Beware stray edits to whitespace (spaces, tabs, line returns)
Merge often
master:
text
Stash
git stash list
git stash show -p stash@{0}
Git Learning: 10.08.2023
Tree-ish:
SHA-1 hash
minimum 4-8
HEAD pointer reference
git show HEAD
git ref/head/master
Ancestry Parents ->
de146^
HEAD^
master^
or
HEAD~1, HEAD~
git show HEAD^
ancestry granparents ->
de146^^
HEAD^^
master^^
HEAD~2
git show HEAD^^
de14621f^^^
HEAD^^^
master^^^
HEAD~3
git show HEAD~3
tree:
blob= binary large object
tree is directory
git ls-tree HEAD
git ls-tree HEAD IOT_final_project/
git log -3
Git Stash(Something like drawer)
steps:
Save changes in stash:
git stash save “temp”
we can make any name to temp to find it later
git help stash command to see what options are available for stash
git stash does not keep untracked files for that need to check gitsh stash help
git stash -u or git stash –include-unteacked
View stashed change:
git stash list
stash@{0}: WIP on main: 6d50117 IOT Project with RIOT Application and MQTT Publisher Client
git stash show stash@{0}
Retrieve stashed changes:
stash is available all of the branches
git stash pop (as only one stash was there)
but if many stash
git stash pop stash@{0}
git stash list (it will not show now) as it is already back
git stash save “changed”
git stash apply
Clear git stash:
git stash drop stash@{0} (newest item is 0 and older is 1)
git stash list
git status
git stash clear (clear all item in stash
Setup a github account:
https://github.com
Setup a folder ready to push to remote
pwd
git remote
git remote add origin https://jj.git
git remote
git remote -v
cat .git/config
git remote rm origin
git remote
git remote add origin http://dh.git
git branches
git checkout master
git push -u origin master (create a branch in remote name master)
git branch -r (show remote branches)
git branch -a (show all kind of branches)
inside git folder
ls -la .git/refs/remotes
cat .git/refs/remotes/origin/master (it is a pointer that points to a tip)
Clone a remote repository
cd ..
ls
git clone https//uuf.git lynda_version
git branch -r
Track remote branch
cat .git/config
check the file to track
-u is for unteacked files
git branch non_tracking
git push origin non_tracking
git branch -u origin/non_tracking non_tracking
cat .git/config
git branch –unset-upstream non_tracking
26.09.2023
Push changes to remote
git commit -am “Fix a bug in the login functionality Test Msg”
git diff origin/master..master
git diff –color-words HEAD..master
–color-words: This option tells Git to display the differences at the word level and use color to highlight the changes. Words that were added will typically be displayed in one color (often green), and words that were removed will be displayed in another color (often red).
Git learning by me :
git revert HEAD~1
HEAD~1: This references the commit immediately before the current HEAD. HEAD typically points to the most recent commit on the current branch, and HEAD~1 refers to the commit just before that.
When you run git revert HEAD~1, Git will create a new commit that contains changes that reverse the modifications made in the most recent commit (HEAD~1). This is useful when you want to undo a previous commit but still keep a record of the fact that you reversed those changes.
After running the command, Git will open your default text editor (usually Vim or Nano) for you to enter a commit message describing the purpose of the revert. Once you save and close the commit message, Git will create a new commit that effectively undoes the changes from the previous commit, and your branch will be updated accordingly.
This is a safer way to undo changes than using a hard reset (git reset –hard) because it preserves the commit history and is less likely to cause data loss.
git reset –soft HEAD~2
git reset: This command is used to reset the branch to a specific commit or point in history.
–soft: This option specifies a “soft” reset, which means that Git will move the branch pointer to the specified commit, but it won’t modify your working directory or staging area. Your changes will remain staged and ready to be committed again.
HEAD~2: This is the commit reference to which you want to reset the branch. HEAD~2 refers to the commit two steps back from the current HEAD commit. So, you’ll effectively move your branch back by two commits.
Fetch changes:
Fetch before wou working
Fetch before you push
Fetch before you go offline
Fetch often
git fetch vs git pull:
git fetch and git pull are both Git commands used to update your local repository with changes from a remote repository, but they work differently.
git pull = git fetch + merge
Merged in fetched changes:
git checkout master
Fast forward
git merge test-branch-from-local
Non fast forward:
git merge –no-ff test-branch-from-local
https://www.linkedin.com/learning/git-branches-merges-and-remotes/merge-in-fetched-changes?autoplay=true&resume=false&u=103775466
git fetch
git merge r
Check out remote branches:
git branch -r
git branch non_tracking (automatically create based on master)
git branch non_tracking origin/non_tracking(but i want to create something else which is not from master obviously)
check status:
git log –oneline -5 non_tracking
cat .git/config
To delete:
git branch -d non_tracking
git branch -b non_tracking origin/non_tracking(create branch and checkout directly)
git checkout master
To avoid git merge conflict/if git rejects it: The workflow could be like:
git fetch->git merge-> git push
Delete a remote branch(do with caution): It is needful when a feature branch is complete and merged
Remove a branch from the remote repository
git branch -r
git push origin :non_tracking (delete in remote)
git branch (still in local but removed in remote)
git push origin –delete non_tracking (delete in remote)
Contribute in opensource project:
Fork it, work on it locally and push.
Check issues and pull requests -> take up a project and announce and talk about it
Workflow:
my: git checkout master > git fetch > git merge origin/master > git checkout -b feedback_form > git commit -m “Add user” > git fetch > git push -u origin feedback_form
lynda: git checkout master > git fetch > git merge origin/master > git checkout -b feedback_form origin/feedback_form > git log > git show 84b6adf0 > git commit -am “Add tour to user” > git fetch > git push
Then me again:
git fetch > git log -p feedback_form..origin/feedback_form > git merge origin/feedback_form > git checkout master > git fetch > git merge origin/master > git merge feedback_form > git push
Git Alias(to type fewer key strokes):
st = status
co = checkout
ci = commit
br = branch
df = diff
dfs = diif –staged
logg = log –graph –decorate –oneline -all
you can put all it in cat ~/.gitconfig
git config –global alias.st status
Setup SSH keys for remote login
You find the more advanced course like: Git Intermediate Techniques( Git pruning branches, working with tags, applying patches, rebasing, cherry picking commits, squashing etc.
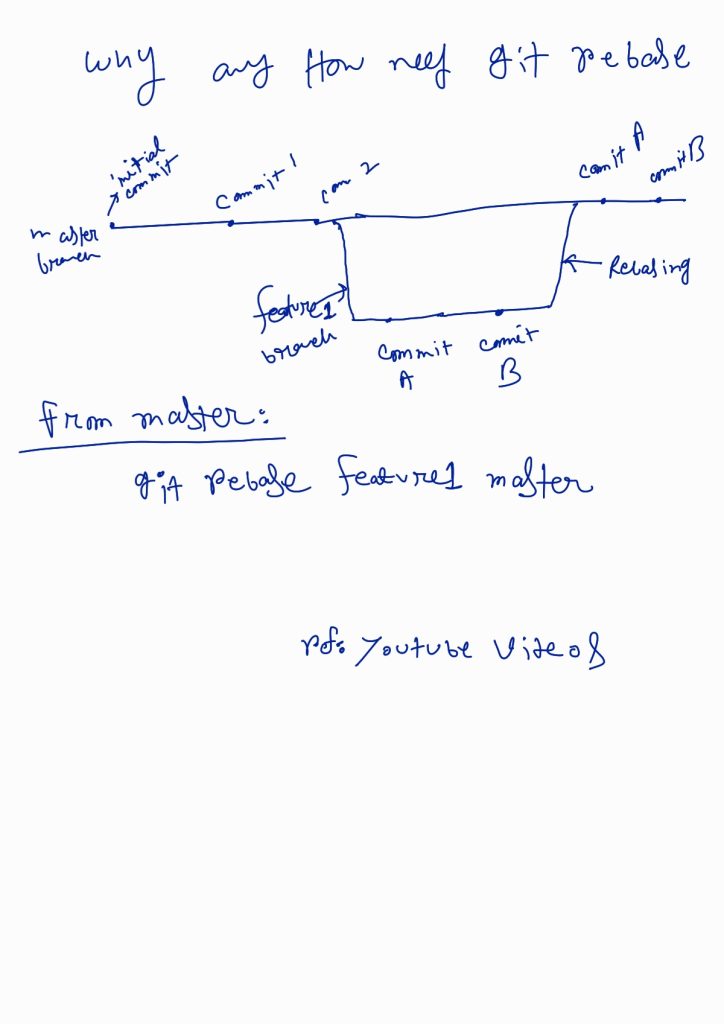
Git Rebase:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yyNySJctW2Y
Merge vs Conflicts:https://www.youtube.com/shorts/nzv0sbfprJo
Solve conflict: https://www.youtube.com/shorts/nzv0sbfprJo